Commentary:
1. There is anticipation of interest rate reductions globally ahead. Such a move impacts the debt funds short term. This is because the price of debt instrument is usually 100-the coupon rate, which is the associated interest rate. So, when the interest rate falls, the bond price goes up accordingly and vice versa. The bond funds tend to leverage this move for their investors. This report serves as a basline for comparison later as the interest rates fall as to how the funds fare better as a result.
While Value Research recognizes 486 debt funds as on the day, when it comes to 19 different sub types, the total goes to 577, the discrepency of 91 more seems to be stemming from the fact that certain funds are double counted across the sub types, which does not hurt our analysis. But, like to report this anamoly though.
2. The individual investors rarely leverage debt funds. It is usually for very high net worth individuals and institutions to leverage for fixed income. The individual investors find it easy to participate in bonds by investing in hybrid funds which is a various mix of equity and bonds.
The following types of debt funds can be found:
Liquid Funds :
Ideal for short-term investments with high liquidity. They invest in very short-term debt instruments,
with portfolio maturity of less than 91 days. A good alternative to savings bank account; potential to offer higher post-tax returns.
Income Funds :
These funds are suited for regular income and invest in a mix of government and corporate securities.
Ultra Short-Term Funds :
Aimed at investors with a short-term horizon, these funds invest in debt instruments with shorter maturities.
Ulta Short Term bonds are Low duration funds, with portfolio maturity of less than a year. Ideal for parking short-term surplus money; also offer slightly better returns than liquid funds.
Short-Term Funds: Medium duration funds where portfolio maturity ranges from one year – three years. Investors with a horizon greater than one year can benefit from these funds in a rising interest rate scenario
.
Long Term Funds: Medium to long duration funds with portfolio maturity between three and 10 years. Suitable for investors with a longer investment horizon. These funds benefit when interest rates fall as bond prices (NAVs) and interest rates are inversely correlated.
Gilt Funds :
These invest primarily in government securities and are considered low-risk.
Medium to long duration funds with portfolio maturity between three and 20 years and negligible credit risk
Dynamic Bond Funds :
Managed actively to adapt to the changing market conditions, by reducing the portfolio maturity in a rising interest rate environment and increasing portfolio maturity in a falling interest rate environment. They have the potential to offer higher returns.
Ideal for investors who may find it difficult to judge the interest rate movement. These funds help investors minimize interest rate risk as they offer flexibility to alter the portfolio maturity according to the interest rate scenario. Maturity is longer when interest rates fall and shorter when interest rates rise.
Credit Opportunity Funds :
Invest in debt instruments with varying credit qualities, potentially providing higher returns with higher risk.
These funds purchase bonds in lower rated bonds to generate higher returns/yields. Suitable only for investors with a profile to take higher risk as investing down the rating spectrum adds to the risk of the portfolio.
Fixed Maturity Plans (FMPs) :
Close ended funds with a fixed maturity date, providing a clear investment horizon. Passively managed.
An alternative to FDs with investment horizon of over three years.
Corporate Bond Funds :
Potentially offering higher returns than government securities
Monthly income Plans (MIPs): Medium to long duration funds normally with exposure of less than 30% to equity. Ideal for investors who are looking for returns better than traditional debt instruments and do not want higher exposure to equities. The tilt towards debt ensures stability of income and the equity portion provides appreciation when stock markets rise.
Capital Protection Oriented Funds (CPFs): Follow an investment structure which seeks to protect the initial investment from capital erosion. These type of scheme offered is “oriented towards protection of capital” and “not with guaranteed returns”. The orientation towards protection of the capital originates from the portfolio structure of the scheme and not from any bank guarantee, insurance cover etc. CPFs have a small equity component which gives risk-averse investors an opportunity to participate in the equity markets without worrying about erosion of the principal which is protected. CPFs are also rated by credit rating agencies.
Floating Rate Funds (FRF): FRFs are a variant of income funds with the primary aim of minimising the volatility of investment returns that is usually associated with an income fund. FRFs invest primarily in instruments that offer floating interest rates. Floating rate securities are generally linked to the Mumbai Inter-Bank Offer Rate (MIBOR), i.e., the benchmark rate for debt instruments. The interest rate is reset periodically based on the interest rate movement. The objective of FRFs is to offer steady returns to investors in line with the prevailing market interest rates.
Overnight Funds: These funds invest in securities having a maturity of 1 day, typically money market instruments. These funds aim to provide liquidity and convenience, rather than high returns. They are suitable for investors (mainly corporate treasuries) looking to park funds for a very short period.
Low-Low Duration Funds: These funds are moderately risky and provide reasonable returns. They are useful for those looking to invest for around 6 months to one year. Their portfolio may include bonds with a weaker credit rating to kick up yields.
Short-Duration Funds: These funds invest in a judicious combination of short and long-term debt, as well as across credit ratings. These funds are recommended for investment horizons of 1-3 years. They usually earn higher returns than liquid and ultra-short duration funds but also show more NAV fluctuations.
Money Market Funds: These funds invest in debt instruments with a maturity of up to one year. They aim to generate returns from interest income, while their slightly longer duration offers some scope for capital gains.
Credit Risk Funds: These funds invest a minimum of 65% of total assets in corporate bonds rated AA or below. That is why they usually generate higher yields as compared to the more conservative corporate bond funds. Investors who are willing to take on higher default risk may consider investing in credit-risk funds.
Banking and PSU Funds: These funds invest at least 80% of total assets in debt instruments issued by banks, PSUs, and public financial institutions. This is a moderate-risk product that seeks to balance yield, safety, and liquidity.
3. In the summary table above, the overall average return of all the debt funds are given for the timeline 1W thru 1Y, and the same is given by 19 debt fund subtypes. Where the sub type fund returns is equal or better than the overall in a timeline, such return is marked in green, else in red.
4. The sub-type funds returns are sorted by the overall ranking, based on the rank average across the return ranks from 1W thru 1Y. The return ranking of each sub-type is marked in the right side for each time line too.
5. Debt Funds Performance Summary by Sub Type
In each sub-type funds table below, if the number of funds are more than 50, only the top 50 based on monthly return are shown. All tables sorted by reducing monthly return. The rows in green are those with above average return in all timelines from 1M thru 1Y. The rows in amber are the ones with above average return in timelines 1M thru 1Y except for one timeline.
5.1. Long Duration Debt Funds
5.2. Dynamic Bond Debt Funds
5.3. Gilt Debt Funds
5.4. Others (US Treasury Bonds)
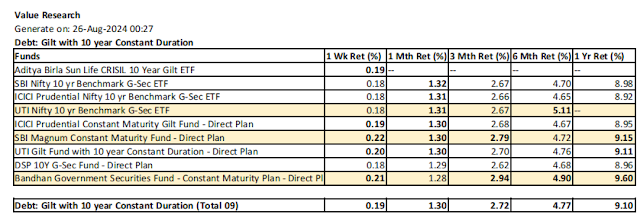
5.5. Gilt with 10 Year Constant Duration
5.6. Medium to Long Duration
5.7. Floater
5.8. Target Maturity
5.9 Medium Duration
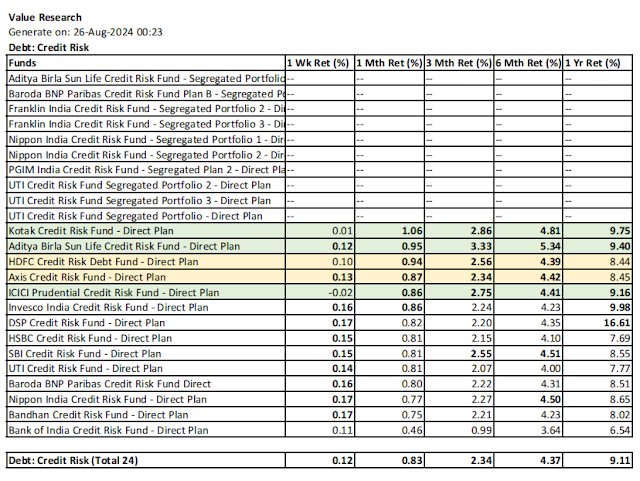
5.10 Credit Risk
5.11. Corporate Bond
5.12. Banking & PSU
5.13. Short Duration
5.14 Low Duration
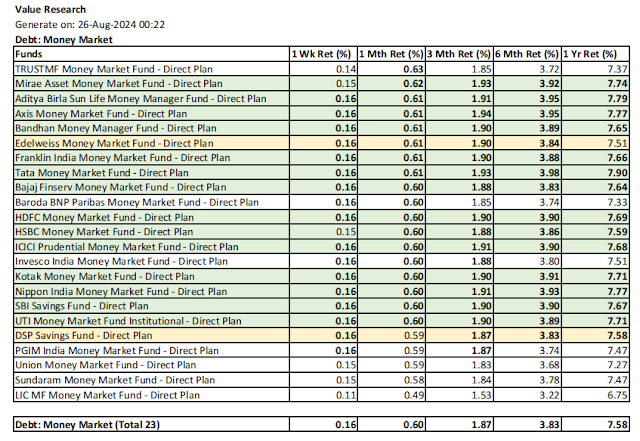
5.15. Money Market
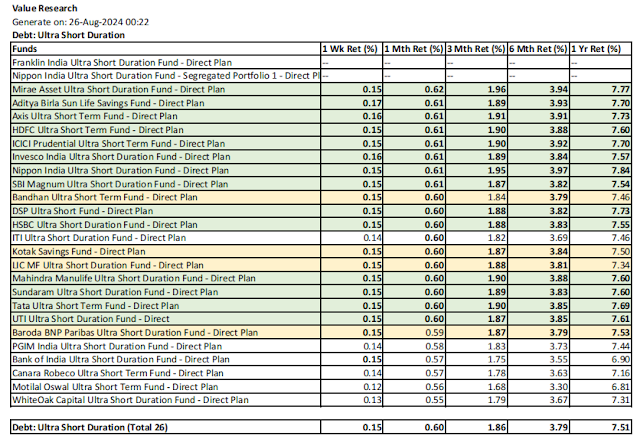
5.16. Ultra Short Duration
5.17. Liquid
5.18. Fixed Maturity
5.19. Overnight
Disclaimer:
- This is not a solicitation for mutual fund investment nor an advice. It is only an insight to help investment decisions based on the free MF performance data downloaded from Value Research. Investment decisions are only yours to make.
- Mutual fund investments are subjected to market risk. Read the propsectus of a mutual fund for all the risk information associated prior to investment.
- The author can not be responsible for the ommissions or errors in the data from Value Research or the data processing errors if any by the author.
- All your investment decisions need to be based on your decision finally, with no blame to anyone else later.
















No comments:
Post a Comment